PROSTATE
xxx
LOW TESTOSTERONE
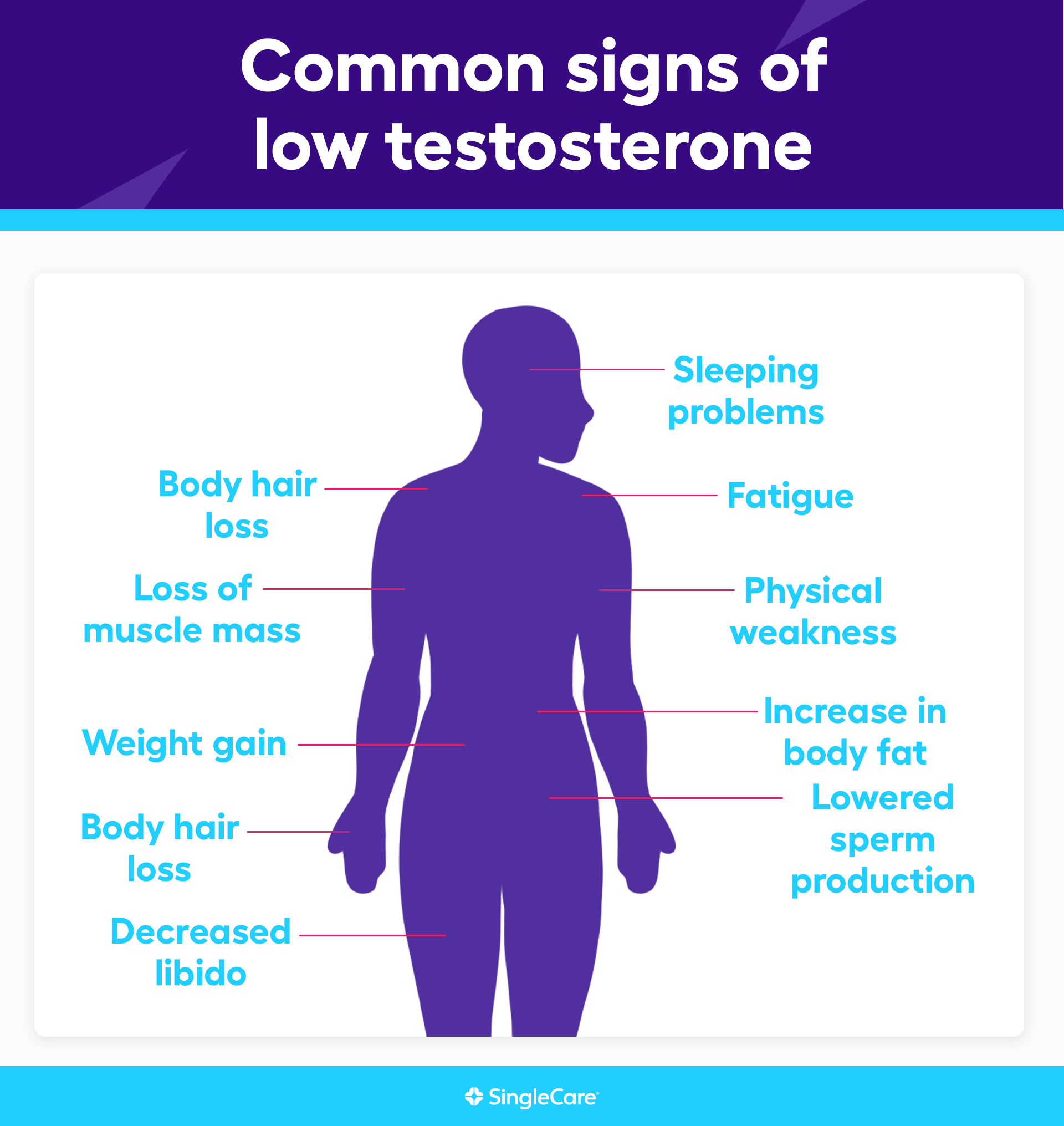
Low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism, can manifest through various signs and symptoms, which may differ depending on age and individual circumstances. Common signs of low testosterone in adults assigned male at birth include:
- Reduced sex drive: Testosterone plays a significant role in libido.
- Erectile dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Loss of body hair: Including armpit and pubic hair.
- Decreased bone density: Which can lead to osteoporosis.
- Decrease in muscle mass: While there may be an increase in body fat.
- Fatigue: A significant drop in energy levels.
- Mood changes: Such as depression or irritability.
- Difficulty concentrating: And other cognitive challenges.
PROSTATE ENLARGEMENT
Prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition that can block the flow of urine due to the enlargement of the prostate gland. Here are some key points about BPH:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting urination or straining while urinating
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Inability to empty the bladder completely
- Blood in urine
- Urinary incontinence
xxx

xxx
ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. It can stem from a variety of physical and psychological factors, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hormonal imbalances, stress, anxiety, and depression.
Symptoms often include persistent trouble with erections, reduced sexual desire, and difficulties in maintaining an erection during sexual activities. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests, and other assessments to identify underlying causes.
Treatment options vary, ranging from oral medications like Sildenafil and Tadalafil, to therapies such as penile injections, hormone therapy, and even surgical implants. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and managing stress, can also be beneficial.
Cooled ThermoTherapy™ For BPH
Cooled ThermoTherapy™ is a safe, non-surgical 30-minute in-office therapy which provides long-term relief from BPH symptoms and urinary obstruction without the side effects and high cost of chronic BPH medication or the risks and high costs associated with invasive surgery.
This treatment option delivers targeted heat to reduce excess prostate tissue and includes an advanced urethral cooling system providing enhanced protection for the healthy urethra as well as increased patient comfort. The treatment typically results in significant improvement from bothersome symptoms such as persistent day time urination as well as reduction in how often you have to get up at night to urinate.
xxx
Watch this video provided by our partners at Urologix


